Why Does HIFULL® HB-139B Overshadow Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fumed Silica in Epoxy Wind Power Adhesive?
In the field of high-end adhesives, fumed silica serves as a core rheology control agent, and its performance directly determines the product’s application properties, storage stability, mechanical properties, and end-use effects. Thanks to its nano-scale particle size and high specific surface area that enable three-dimensional network construction, fumed silica has become the key material for regulating the rheological behavior of adhesives.
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic fumed silica exhibit distinctly different thickening and thixotropic properties in epoxy systems due to differences in surface chemical properties.
As a new type of material, HB-139B is a hydrophobic fumed silica product derived from hydrophilic fumed silica treated with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). It possesses excellent thickening and thixotropic properties as well as stability in epoxy resin systems, making it particularly suitable for high-thickening and high-reinforcement systems such as wind turbine blade adhesives.
HIFULL® HB-139B
HIFULL hydrophobic fumed silica HB-139B has achieved dual breakthroughs over the hydrophilic HL-200 and hydrophobic HB-139 in two core indicators, rheological properties and thickening performance, through optimized surface treatment technology and microstructure.
Based on rheological curve experimental data and industrial application cases, this article systematically analyzes the technological innovation and market value of HB-139B.
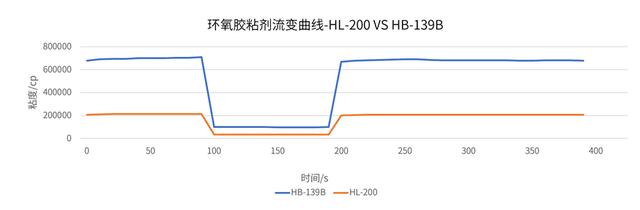
HB-139B vs. HL-200: A Showdown of Rheological Properties Between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fumed Silica
The same proportion of hydrophobic fumed silica HB-139B and HL-200 was added to epoxy wind power adhesives, and a rotational rheometer was used to test their viscosity and thixotropy. Technicians found that at the same addition level, the initial viscosity of the epoxy wind power adhesive with HB-139B can reach approximately 700,000 cp, while that of HL-200 is 200,000 cp, about 3.5 times higher. High viscosity can establish a three-dimensional network structure in epoxy adhesives faster and more effectively, which is crucial for inhibiting filler settlement and maintaining storage stability.
In the thixotropy test, the viscosity decrease rate and recovery rate of HL-200 were significantly lower than those of HB-139B. During the gluing process, HB-139B can ensure the adhesive sets quickly after application, directly translating into better anti-sagging performance. It guarantees uniform adhesive layer thickness during vertical surface construction, reduces dripping and sagging, and improves construction efficiency, quality, and appearance.
Meanwhile, the viscosity curve of HB-139B remained more stable throughout the test period. It can provide more durable and reliable viscosity retention under static storage or low-shear conditions, reducing batch differences and storage risks.
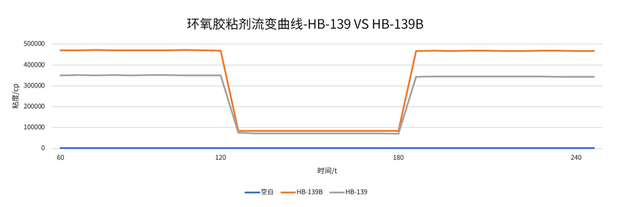
HB-139B vs. HB-139: A Contest of Thickening Performance Among Hydrophobic Fumed Silica
The thickening mechanism of hydrophobic fumed silica stems from hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and interactions between particles. The degree of surface modification directly affects its dispersibility and network construction ability in the epoxy matrix, as can be seen from the rheological curve:
At the same addition level, the initial viscosity of HB-139B is approximately 470,000 cp, while that of HB-139 is about 350,000 cp, which is 1.34 times higher. This indicates that HB-139B has significantly better thickening effect than HB-139.
It shows that through optimized surface hydrophobic modification (such as modification with specific silane coupling agents), HB-139B enhances the dispersibility and interaction sites of particles in the epoxy matrix, achieving higher system viscosity at the same addition amount.
From the rheological performance showdown with the hydrophilic HL-200 to the thickening performance contest with the hydrophobic HB-139, HB-139B has demonstrated unique value in epoxy wind power adhesive formulations with superior thickening efficiency and more stable thixotropy. Its performance advantages are not only reflected in laboratory rheological curves but also translated into practical application benefits, such as easy construction, no sagging, and high storage stability.
HB-139 Properties and Functional Applications
In fields with strict requirements for adhesive performance, such as high-end electronic packaging, wind turbine blade bonding, and aerospace structural adhesives, the application of HB-139B will drive epoxy adhesives toward a more efficient and reliable direction. This is not only a technological breakthrough for a fumed silica product but also a vivid practice of material innovation empowering industrial upgrading.
When the surface modification of micro-particles achieves precise matching with macro-rheological properties, the application boundaries of epoxy adhesives will be redefined, providing a solid theoretical foundation and technical support for “domestically substituted new material solutions” in the high-end manufacturing field.