The Rheological of HB-139 in Two-Component Epoxy Steel-Bonding Adhesives
Epoxy steel-bonding adhesive is a two-component structural adhesive specifically designed for building reinforcement. It is primarily used to bond steel plates onto concrete structural elements (such as beams, columns, and slabs). Through the synergistic action of steel and concrete, it enhances the load-bearing capacity, stiffness, and ductility of these components.
This adhesive is widely applied in structural strengthening and seismic retrofitting projects. Its core formulation consists of an epoxy resin matrix combined with curing agents, toughening agents, fillers, and other additives, resulting in a high-strength, high-bonding, and durable adhesive layer.
As a high-performance two-component (A/B) epoxy structural adhesive, the A component of epoxy steel-bonding adhesive is primarily based on epoxy resin and contains toughening agents and fillers. Due to its inherently high viscosity, thixotropy is essential to prevent sagging during vertical application. The B component mainly comprises amine-based curing agents and has a relatively low base viscosity; without sufficient thixotropy, it tends to sag during application, compromising adhesive layer uniformity. Therefore, fumed silica is commonly added to both A and B components in practical applications to tailor their rheological properties.
HIFULL® HB-139B
Hydrophobic fumed silica HB-139 is a nano-sized silica powder surface-modified with hydrophobic groups, exhibiting strong affinity toward organic solvents and resins. When dispersed in non-polar or weakly polar systems, its surface silanol groups (Si–OH) and hydrophobic moieties form a three-dimensional network structure via hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces, imparting significant thickening, excellent thixotropy, good anti-settling performance, and superior hydrophobicity to the system.
Researchers at HIFULL investigated the influence of varying HB-139 dosages on the thickening and thixotropic behavior of both A and B components, revealing its mechanism of action and engineering value.
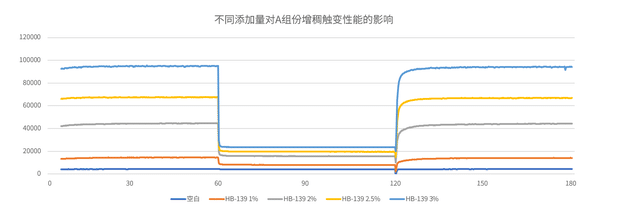
Figure 1 illustrates the effect of different HB-139 addition levels (1%, 2%, 2.5%, and 3%) on the thickening and thixotropy of the A component. The horizontal axis represents test time corresponding to shear stress variation, while the vertical axis shows viscosity (higher values indicate greater viscosity).
Experimental data reveal: the blank sample (A component without fumed silica) exhibited almost no change in viscosity throughout the test and displayed the lowest viscosity among all five tested samples.
In contrast, samples containing fumed silica showed clear viscosity changes, indicating that the addition of fumed silica imparted thixotropy—namely, the three-dimensional network temporarily breaks down under high shear (e.g., mixing or troweling), causing a sharp drop in viscosity, and rapidly rebuilds once shear ceases, restoring viscosity.
Moreover, as the HB-139 dosage increased from 1% to 3%, the viscosity of the A component continuously rose, and the magnitude of viscosity change under identical shear conditions also increased, signifying enhanced thixotropic index.
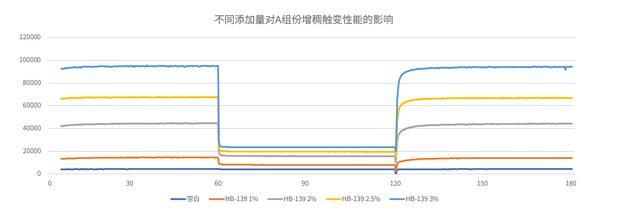
Similarly, the thickening and thixotropy curves for the B component (Figure 2) follow the same general trend but exhibit fundamental differences.
First, the base viscosity of the blank B component is lower than that of the blank A component due to the more fluid nature of the curing agent system.
Second, although viscosity increases with HB-139 addition, the magnitude of increase is significantly smaller than in the A component, and the enhancement in thixotropy is also less pronounced.
Nevertheless, HB-139 effectively improves the static viscosity and thixotropy of the B component, which increases with dosage, helping to reduce its inherent flow tendency and ultimately contributing to the overall workability of the mixed adhesive.
HB-139 Properties and Functional Applications
The application of hydrophobic fumed silica HB-139 in epoxy steel-bonding adhesives vividly demonstrates the engineering wisdom of “small materials solving big problems.” As the “reinforcing tendons” of building structures, every incremental performance improvement in epoxy steel-bonding adhesives directly impacts structural safety. High-performance nano-additives like HB-139 are providing more efficient and reliable material solutions for modern structural reinforcement engineering.