HIFULL®Fumed Silica For Intelligent Control Power Battery Adhesive
With the booming development of the new energy vehicle industry, the safety and stability of power batteries are of paramount importance. As a key material for connecting battery components, the performance of power battery adhesives directly impacts the overall performance of the battery.
Fumed silica, a commonly used functional additive, enhances the thickening and thixotropic properties of adhesives, positively influencing the controllability, workability, and stability during the encapsulation process.
HIFULL Technical experts have conducted in-depth research on polyurethane-based power battery adhesives, investigating the effects of different fumed silica dosages and various brands of fumed silica (at the same dosage) on the thickening and thixotropic behavior of these adhesives. Pioneering the concept of a “golden ratio” in power battery adhesives, they continuously optimize formulations and data to intelligently regulate adhesive viscosity and thixotropy. This innovation aims to overcome the technical challenges of difficult and inefficient encapsulation in battery manufacturing processes.
Battery
Fumed silica is a nano-scale inorganic new material with an exceptionally large specific surface area and high surface activity. When incorporated into polyurethane adhesive systems, the silanol groups on its surface form a three-dimensional network structure that increases the adhesive’s viscosity. Under external shear forces, this network structure breaks down, reducing viscosity and improving flowability for easier application. Once the shear force is removed, the hydrogen-bonded network gradually reforms, restoring viscosity and demonstrating thixotropic behavior.
Additionally, variations in fumed silica dosage and brand characteristics influence the properties and formation of this hydrogen-bonded network, thereby producing different effects on the thickening and thixotropic performance of power battery adhesives.
If the dosage is too low, the desired viscosity and thixotropy cannot be achieved, while excessive amounts may lead to material embrittlement or structural collapse (affecting other material properties).
So, what trends and characteristics will variations in fumed silica bring to polyurethane adhesives? The technical team at Hubei Huifu Nanomaterial Co., Ltd. conducted a series of experiments and investigations to explore this.
In the experiments, Component A primarily consisted of a premix containing fumed silica, polyols, fillers, and additives, while Component B was composed of a premix of fumed silica, polyisocyanates, prepolymers, and fillers. Both components were thoroughly dispersed at 2000 rpm for 30 minutes in a vacuum disperser before being mixed at a 1:1 ratio and cured to form the final polyurethane power battery adhesive.
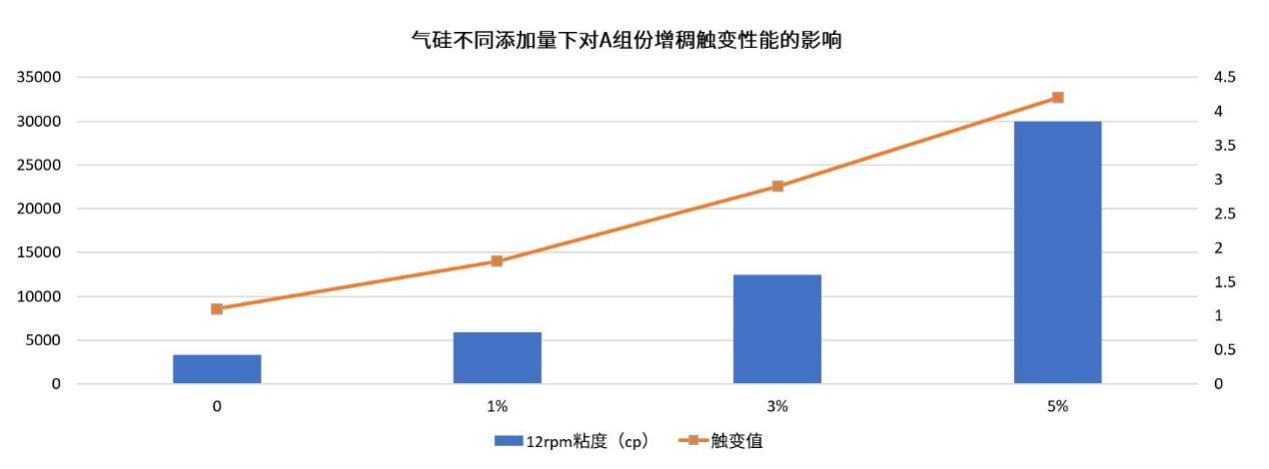
In Component A, HIFULL® fumed silica was added at 1%, 3%, and 5% respectively. As shown in the graph, the viscosity of Component A increased with higher fumed silica content, but the rate of increase varied even at the same incremental dosage. The data revealed that the baseline viscosity (without fumed silica) was 3,303 Pa·s, while the viscosities at 1%, 3%, and 5% additions were 5,872 Pa·s, 12,456 Pa·s, and 29,993 Pa·s, respectively. When the dosage increased from 1% to 3%, viscosity rose by 112%, whereas increasing from 3% to 5% resulted in a 141% viscosity increase, indicating an accelerated growth trend.
The baseline thixotropic index (without fumed silica) was 1.1, while the values at 1%, 3%, and 5% additions were 1.8, 2.9, and 4.2, respectively. When increasing from 1% to 3%, the thixotropic index grew by approximately 61%, but from 3% to 5%, the increase was only about 45%, showing a declining growth rate, unlike the viscosity trend.
Thus, in Component A, increasing the fumed silica dosage proportionally enhanced both viscosity and thixotropic index, but their growth patterns differed.
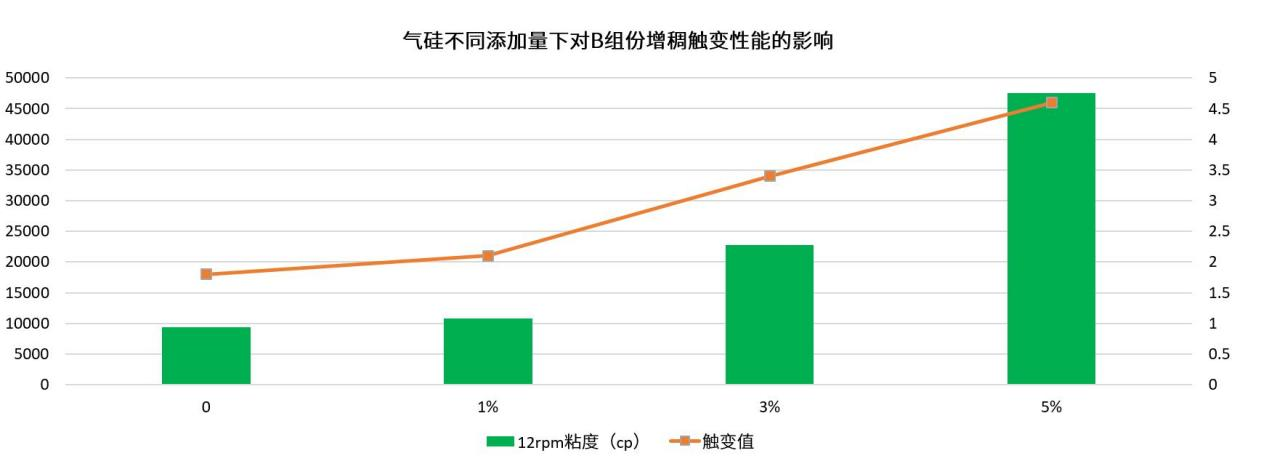
In Component B, HIFULL® fumed silica was added at 1%, 3%, and 5% respectively. As shown in the figure, the viscosity of Component B increased with higher fumed silica content. The data shows that the baseline viscosity (without fumed silica) was 9,412 Pa·s, while the viscosities at 1%, 3%, and 5% additions were 10,809 Pa·s, 22,829 Pa·s, and 47,590 Pa·s respectively. When the dosage increased from 1% to 3%, viscosity rose by 111%, and when increasing from 3% to 5%, the viscosity increased by 108%, showing a slight decline in the growth rate.
The baseline thixotropic index (without fumed silica) was 1.8, while the values at 1%, 3%, and 5% additions were 2.1, 3.4, and 4.6 respectively. When increasing from 1% to 3%, the thixotropic index grew by approximately 62%, but from 3% to 5%, the increase was only about 35%. Similar to the viscosity trend, the growth rate of the thixotropic index decreased.
These results demonstrate that in Component B, increasing the fumed silica dosage proportionally enhanced both viscosity and thixotropic index, with consistent trends in their growth patterns.
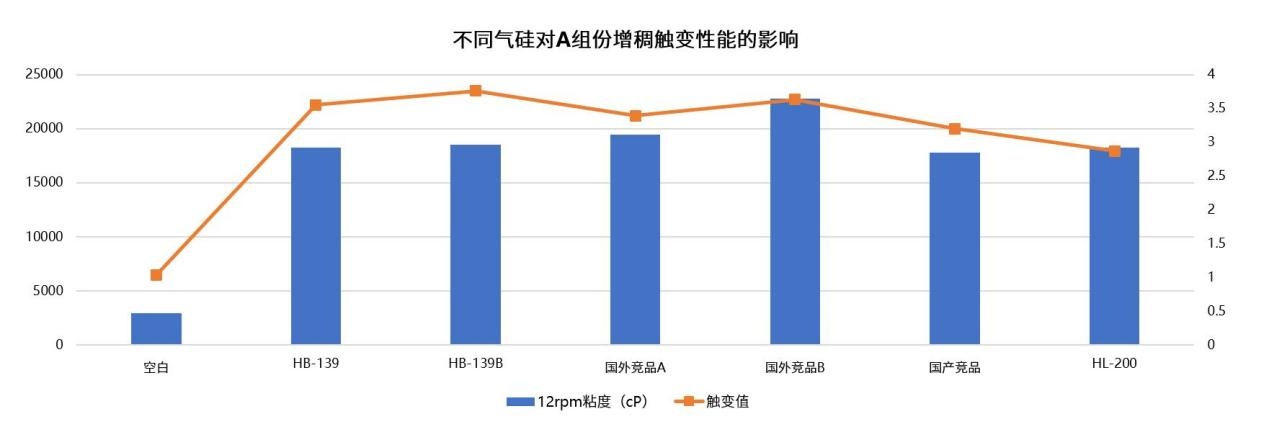
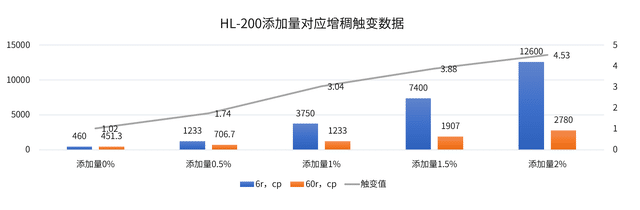
Subsequently, technical team at Hubei Huifu Nanomaterial Co., Ltd. investigated the effects of different fumed silica brands on the thickening and thixotropic properties of polyurethane power battery adhesives at a fixed 3% addition level.
In Component A, tests were conducted on HB-139, HB-139B, foreign competitor A, foreign competitor B, domestic competitor, and HL-200 to evaluate their viscosity and thixotropic performance.
The results revealed variations among different products. HB-139/139B demonstrated better thickening performance than domestic competitors but slightly weaker than foreign competitors. However, HB-139B exhibited superior thixotropic properties compared to both domestic and foreign alternatives.
In Component B, HB-139B showed stronger thickening performance than foreign competitor A but was slightly inferior to foreign competitor B, while its thixotropic performance was comparable to foreign competitors.
In summary, the dosage of fumed silica is a critical factor affecting the thickening and thixotropic properties of polyurethane power battery adhesives. Appropriately increasing the additive amount can effectively enhance both viscosity and thixotropic performance to meet various application and processing requirements.
Meanwhile, different brands of fumed silica exhibit varying effects on adhesive properties at identical dosages due to differences in production processes, particle size distribution, and surface characteristics. In practical applications, the optimal fumed silica dosage and brand selection should be determined based on specific performance requirements and cost considerations.
Looking ahead, Hubei Huifu Nanomaterial Co., Ltd.’s research will further investigate the interaction mechanisms between fumed silica and polyurethane adhesives, refine the “golden ratio” formulation, and develop superior encapsulation solutions for polyurethane power battery adhesives. These advancements will provide more reliable support for the continued growth of the new energy vehicle industry.