HIFULL® Hydrophobic Fumed Silica HB-139 in Adjusting the Consistency of Silicone Adhesives
Silicone adhesives are widely used in numerous fields such as electronics, electrical appliances, construction, automotive, and aerospace due to their exceptional resistance to high and low temperatures, weather ability, electrical insulation, and chemical stability.
Their consistency, as a key performance indicator, directly affects dispensing accuracy, coating uniformity, and mechanical properties after curing. Traditional inorganic fillers (such as light calcium carbonate) can increase the system viscosity through physical filling and adjust rheology, but they suffer from issues like poor dispersibility and easy sedimentation.
Hydrophobic fumed silica has gradually become a key additive for rheological regulation of silicone adhesives, owing to its unique nano-effects and surface modification technology.
Fumed silica is a nanoscale amorphous silica produced by high-temperature hydrolysis of silicon halides in a hydrogen-oxygen flame. Its primary particle size is extremely small (typically 7-40nm), featuring high surface activity, high specific surface area, high thermal stability, and high purity. These particles form a three-dimensional hydrogen bond network through surface silanol groups (Si-OH), like building an invisible three-dimensional net in the colloid, which can effectively restrict the movement of polymer molecular chains, thereby producing significant thickening and thixotropic effects.
When at rest, the silicone adhesive exhibits high viscosity to maintain its shape; when sheared (e.g., during stirring or coating), the viscosity drops rapidly to facilitate construction.
As a representative of HIFULL® hydrophobic fumed silica, HB-139‘s unique value lies in its surface treatment with organosiloxane, where most hydrophilic silanol groups are replaced by non-polar organic groups (such as dimethylsiloxy groups).
This hydrophobic treatment brings multiple advantages to the application of fumed silica:
For this reason, technicians from Hubei Huifu Nanomaterial Co., Ltd. took light calcium carbonate and hydrophobic fumed silica HB-139 as variables to explore the consistency changes of silicone adhesives under different addition amounts of the two.
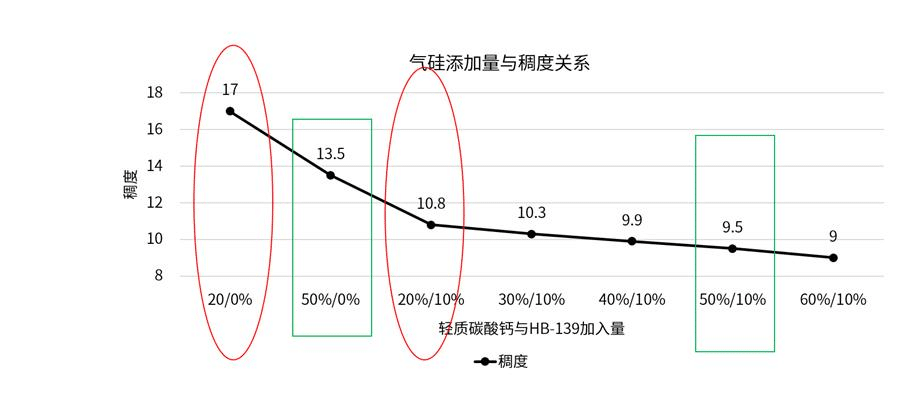
The above figure shows the curve of consistency changes of silicone adhesives with different addition amounts of light calcium carbonate/HB-139 (the horizontal axis is the addition amount of light calcium carbonate and HB-139, and the vertical axis is the consistency).
When no fumed silica is added and only light calcium carbonate is used, the results from the above figure show that the consistencies of silicone adhesives corresponding to light calcium carbonate/HB-139 ratios of 20% /0% and 50% /0% are 17 and 13.5, respectively.
With the light calcium carbonate dosage fixed at 20%, compared with the system without fumed silica, when 10% HB-139 is added, the consistency value of the silicone adhesive decreases from 17 to 10.8.
With the light calcium carbonate dosage fixed at 50%, compared with the system without fumed silica, when 10% HB-139 is added, the consistency value of the silicone adhesive decreases from 13.5 to 9.5. This indicates that the addition of fumed silica can significantly increase the viscosity of the system.
When the addition amount of fumed silica HB-139 is fixed at 10%, as the addition amount of light calcium carbonate increases from 20% to 60%, the consistency changes from 10.8 to 9, with a small variation range.
This shows that the thickening effect of adding fumed silica is significantly better than that of light calcium carbonate.
The addition amount of hydrophobic fumed silica HB-139 has a significant impact on the consistency of silicone adhesives. Without HB-139, light calcium carbonate mainly changes the consistency through filling, with a relatively small impact. After introducing HB-139, its hydrophobic effect and three-dimensional network structure become the dominant factors in consistency regulation.
HB-139 Properties and Functional Applications
In the formulation design of silicone adhesives, according to the actual application process (e.g., high fluidity required for dispensing, consistency adjustment needed for sealing scenarios), the subtle non-linear relationship between its dosage and consistency can be grasped, and the addition amounts of HB-139 and light calcium carbonate can be precisely controlled to optimize the consistency performance.
Meanwhile, further research is needed on the influence of HB-139 addition amount on other properties of silicone adhesives (such as bonding strength and aging resistance) to achieve the optimal matching of the comprehensive performance of the product and promote the wider and higher-quality application of silicone adhesives in various industries.